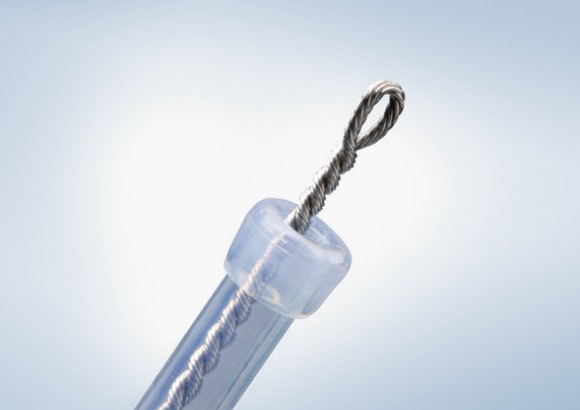
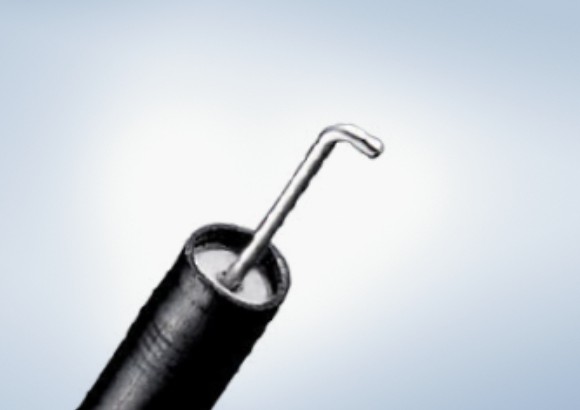
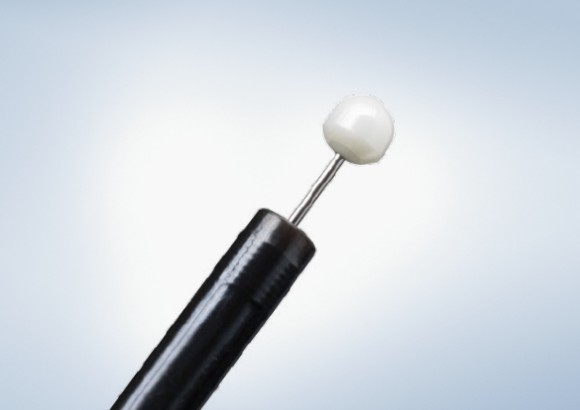
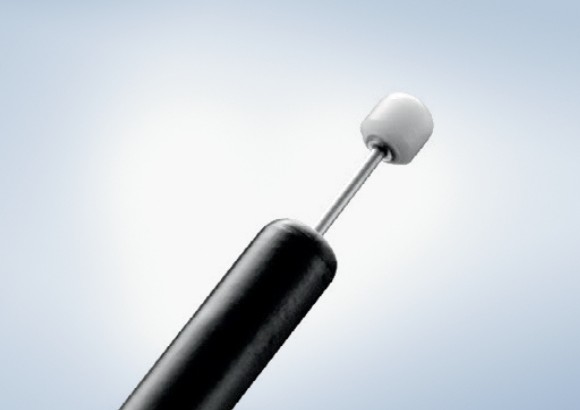
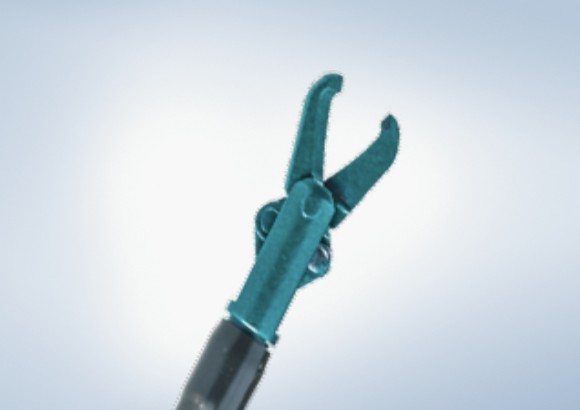
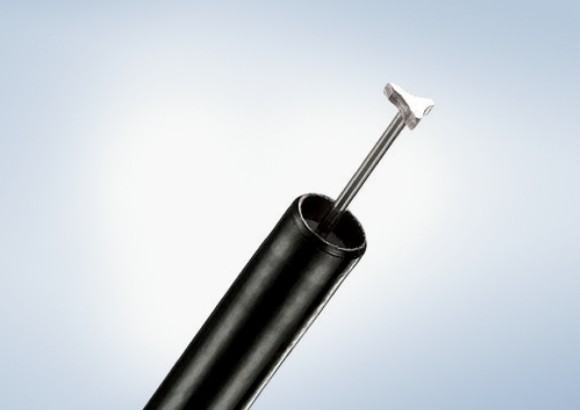
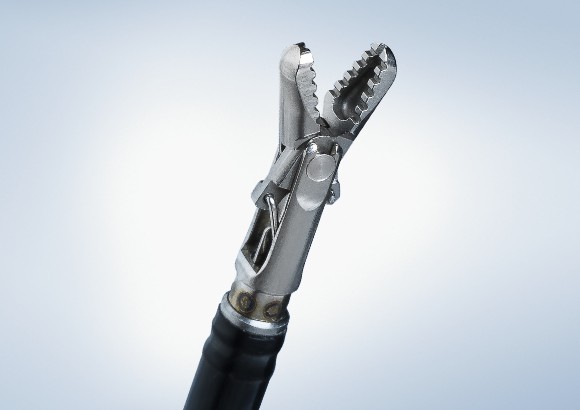
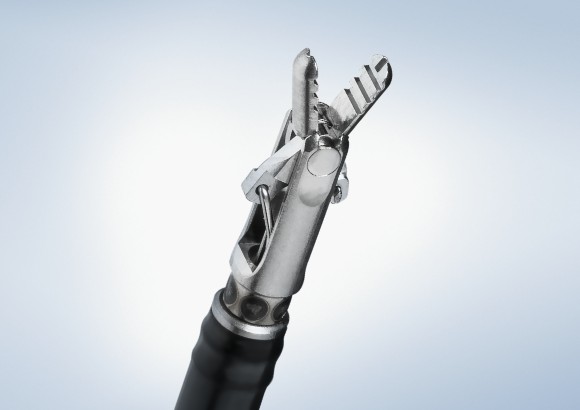
Olympus Advancing Treatment with a large selection of ESD Knives on the Market
Treatment with gastrointestinal endoscopy has evolved rapidly, and Olympus has been there with innovative solutions every step of the way. From polypectomy to endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) to today’s endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), treatment has become both more effective and less invasive.
With the remarkable ability to enable en bloc resection of lesions throughout the gastrointestinal tract, ESD represents a major milestone in this evolution. It offers a potential alternative for open surgery when treating larger lesions. It also has revolutionized the treatment for early gastric cancers, becoming the preferred modality worldwide.1
ESD allows for the removal of the entire tumor or lesion in one piece, leaving the native organ esophagus and stomach intact. It often enables a return to normal function, and in the case of achalasia, patients regain their ability to swallow. Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays, faster recoveries, reduced pain and less expense after ESD compared to open or laparoscopic surgical procedures.2,3,4,5
By eliminating the need for multiple resections, ESD is less likely to leave diseased tissue behind that would necessitate additional surgery, and en-bloc resections enable more accurate histopathologic evaluation and staging. Esophageal and gastric cancers and lesions have a significantly lower recurrence rate after ESD compared to other surgical options.
< 1%
15-20%1
Japan has one of the highest incidence rates of gastric cancers, and in the late 1900s, its physicians began working diligently to find more effective treatments.i To aid in that effort, Olympus partnered with the National Cancer Center Hospital in Japan in the 1990s to collaborate with the country’s physicians in developing knives that helped resolve issues observed during EMR. The result was the introduction in 2002 of the world’s first knife capable of ESD, and a new treatment approach was born.
Following the introduction of the ITknife™ electosurgical knife, Olympus was instrumental in driving ESD adoption by collaborating with key physicians to analyze evidence-based data on the efficacy and safety of ESD.
After identifying areas for expansion, Olympus engineered a broader portfolio of options along with education and training for clinicians. The result is an expansive portfolio of ESD knives and peripherals and a procedure that has significantly advanced the possibilities for today’s minimally invasive surgeries.
-
1998
ITknife electrosurgical
knife prototype -
1999
1st ESD procedure
using prototype -
2002-2005
Market release:
* ITknife electrosurgical knife
(1st on market)
* HookKnife™
electrosurgical knife
* FlexKnife™
electrosurgical knife
* TriangleTipKnife™
electrosurgical knife
* Coagrasper™
hemostatic forceps
* Hot Bite
* Hot Claw -
2006
Market release:
* ITknife 2 electrosurgical knife
(increased safety profile
for knife and procedure
compared to ITKnife) -
2008
Market release:
* DualKnife™
electrosurgical knife
* Coagrasper™ hemostatic
forceps (for colon) -
2010
Market release:
* EndoLifter™ forceps -
2012
Market release:
* ITknife nano™
electrosugical knife -
2014-2016
Market release:
* DualKnife J
electrosurgical knife
* Coagrasper G
hemostatic forceps -
2018
Market release:
* SB Knife™ 3-in-1 knife -
2020
Market release:
* TriangleTipKnife J
electrosurgical knife
* HookKnife J
electrosurgical knife -
2022
Reimbursements
for POEM
Olympus has more than 100 years of experience and expertise in the manufacture of gastrointestinal endoscopy products, and we are known for our industry leadership in innovative technologies.
Starting with our work with physicians in Japan more than 20 years ago to develop knives that allowed the introduction of ESD, our teams continue to work with physicians around the world to offer best-in-class devices to meet every procedural application.
Olympus has a comprehensive portfolio of ESD knives on the market today, and we stay committed to advancing procedural possibilities. With the more recent additions of the
DualKnife J, TriangleTipKnife J and HookKnife J electrosurgical knives, Olympus now offers knives that enable dissection and lifting of the mucosa by injecting saline solution into the submucosal layer. This eliminates the need to change devices, potentially leading to shorter procedure times.
The Olympus ESD portfolio
Olympus drives ESD innovation with unique forward-thinking concepts and devices with reliability, but our partnership with our customers doesn’t stop there. Olympus offers a total solution to help our customers implement and grow their ESD practices.
Our support includes:
Clinical RN specialists to support your ESD/POEM cases while using Olympus devices.
Equipment and procedural training.
Professional education.
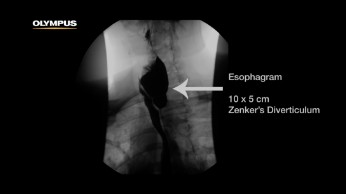
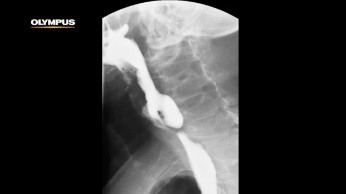
Watch our ESD products
in action with noted physicians:

- NCBI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5824597/
- Abdelfatah MM, Barakat M, Ahmad D, Ibrahim M, Ahmed Y, Kurdi Y, Grimm IS, Othman MO. Long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus surgery in early gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Apr;31(4):418-424. Doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001352. PMID: 30694909.,
- Hu J, Zhao Y, Ren M, Li Y, Lu X, Lu G, Zhang D, Chu D, He S. The Comparison between Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection and Surgery in Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018 Feb 18;2018:4378945. doi: 10.1155/2018/4378945. PMID: 29670651; PMCID: PMC5835246.
- Draganov PV, Aihara H, Karasik MS, Ngamruengphong S, Aadam AA, Othman MO, Sharma N, Grimm IS, Rostom A, Elmunzer BJ, Jawaid SA, Westerveld D, Perbtani YB, Hoffman BJ, Schlachterman A, Siegel A, Coman RM, Wang AY, Yang D. Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in North America: A Large Prospective Multicenter Study. Gastroenterology. 2021 Jun;160(7):2317-2327.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.036. Epub 2021 Feb 19. PMID: 33610532.
- Yang D, Draganov PV. Clinical Updates in Colorectal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):269-271. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.09.025. Epub 2021 Nov 12. PMID: 34774551.