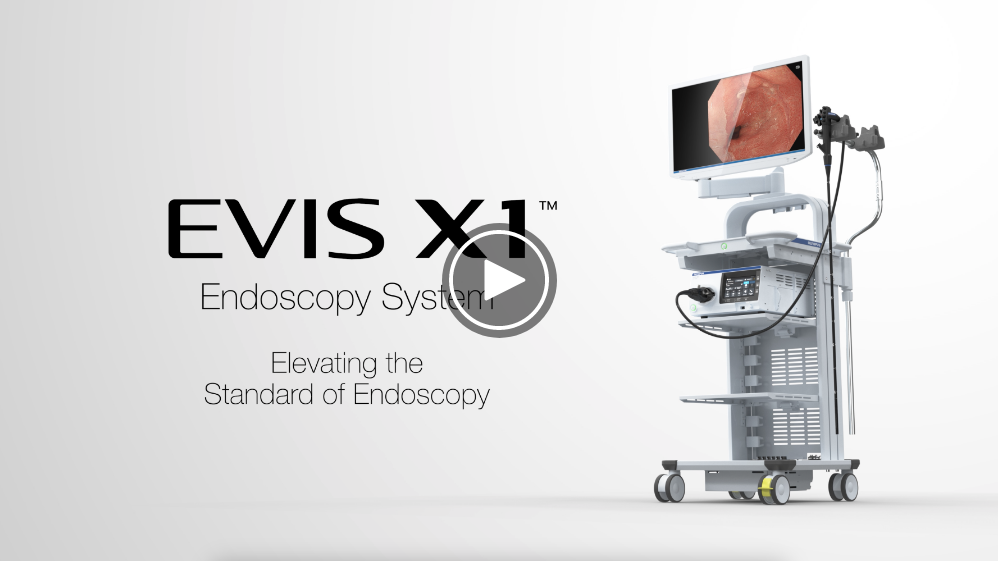
Elevating the Standard of Endoscopy
The EVIS X1 endoscopy system introduces a range of technologies that aim to revolutionize the way physicians can detect, characterize and treat gastrointestinal disorders.
As a leading medical technology company, we want to support every endoscopist.
In every procedure. Every day.
The EVIS X1 endoscopy system provides a combination of diagnostic and therapeutic innovations, alongside well-established technologies, to streamline and improve endoscopic procedures and scope handling.1

The gastrointestinal tract often makes it difficult for a physician to keep their endoscopic image in focus.
Fortunately, Olympus’ latest scope innovation, Extended Depth of Field (EDOF) technology, allows precise observation through continuous broad focus and seamless magnification. The continuously sharp image created by EDOF technology reduces the need for focal adjustments, and enhanced visibility aids in making the endoscopic procedure efficient. It may also support the identification and diagnosis of abnormalities with confidence.2

Available only on the EZ1500 series endoscopes, EDOF technology produces a continuously sharp, high-resolution image with minimal focal adjustments at any point during an endoscopic procedure.2
EDOF technology projects two images with identical content at different focal lengths and combines them into one image in total focus. Light entering the scope’s objective lens is split into two separate beams. The beams are simultaneously projected onto an image sensor to generate a single image with a wide depth of field, thereby reducing the need for focal adjustments during a case.
This technology allows the EZ1500 series scopes to provide closer-focused observation in near and normal modes, as well as higher magnification, than the GIF-HQ190 and CF-HQ190L/I scopes.2 It helps a physician obtain sharp images with minimal focal adjustments, which may aid in their detection and diagnosis in a procedure.2
GIF-EZ1500 gastroscopes.


The global burden of colorectal cancer (CRC) is expected to increase by 60%, or more than 2.2 million new cases and 1.1 million deaths, by 2030.3 Higher detection rates and more accurate diagnoses can help reduce the number of deaths from CRC;4 however, precursor lesions are often tiny and easy to overlook.
With that in mind, TXI technology was designed to increase the visibility of potentially suspicious lesions and polyps by enhancing image color and texture during endoscopic screening.5

A multicenter randomized controlled trial published in Gastroenterology in October 2023 revealed TXI technology significantly improves the adenoma detection rate (ADR) by 13.61%, and the rate of adenomas per colonoscopy (APC) ≥ 5mm in size, versus white light endoscopy (WLE), highlighting its ability to support clinicians in identifying potential precancerous lesions and enhancing the quality of their colonoscopies.6
TXI technology is designed to emphasize image information by combining the three image processing algorithms: brightness correction of the dark part of the image; color difference expansion processing; and texture component emphasis processing.5 The incoming image is split, and the texture and brightness are enhanced before the separate images are merged back together. Additional color enhancements are made to define subtle tissue differences more clearly.7
TXI technology is not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis.
This image is being furnished to provide an example of TXI technology use. The TJF-Q290V used in this case is not available in the United States market at this time, nor is there an established time for its release. The safety and effectiveness of this product and/or the use of this product has not yet been established in the United States market.
RDI™ Technology - The Power to See Deeper


Gastrointestinal bleeding is a serious challenge, involving considerable mortality of 2-10% and high management costs.8 Consequently, prevention of complications is crucial.
RDI technology improves the visibility of bleeding points within the mucosa and enhances the visibility of deep blood vessels compared to white light.5

Identification of bleeding spots through RDI technology makes hemostasis quick and easy.5 Therefore, RDI technology may help to reduce stress and procedure time for emergency bleeding and endoscopic resection.5
RDI technology works by applying the same principle of NBI™ (Narrow Band Imaging™) technology. However, rather than selecting short wavelengths of light (Blue and Green) to view surface patterns and blood vessels, RDI technology uses Green, Amber and Red. These longer wavelengths of light penetrate more deeply into human mucosal tissue.4
RDI technology is not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis.
NBI™ Technology

NBI technology has been shown across multiple studies:
- To reduce procedure time by reducing the number of biopsies taken compared to the Seattle protocol for patients with Barrett’s esophagus9
- To increase adenoma detection rate (ADR) and serrated adenoma detection rate (SADR) compared to white light imaging10,11
- To support accurate prediction of diminutive colorectal polyp histopathology12


Utilizing specific Blue and Green wavelengths absorbed by hemoglobin, high-definition NBI technology enables visual observation of mucosal and vascular patterns. During endoscopic observation, NBI technology enhances visualization of the capillary network and mucosal morphology.5
NBI technology is not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis.
Designed to Improve Scope Handling
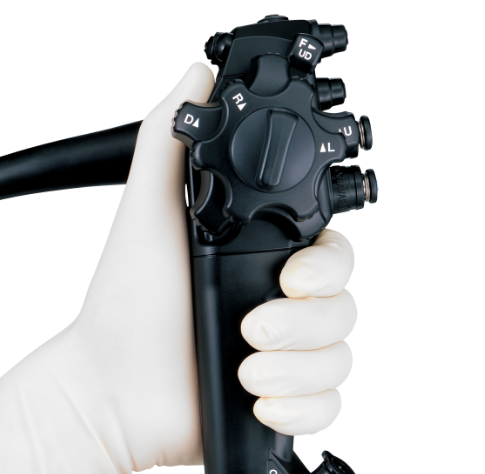


Using a scope with an ergonomic control section may help improve a physician’s operability and may allow them to experience less fatigue during high volume caseloads and lengthy therapeutic procedures.
The ErgoGrip control section of the EVIS X1 scope allows for:
- Designed to improve user comfort and scope handling13
- Easy to reach angulation control knobs and switches to accommodate users with small hands13
- EVIS X1 scope control section weighs 10% less than the EVIS EXERA™ III scope control section13

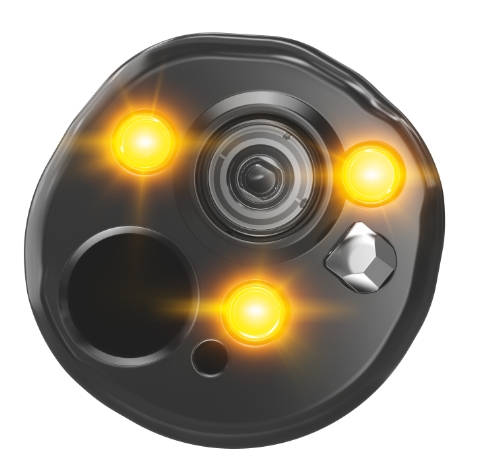
5 LED Spectrum Technology
The CV-1500 video system center combines 5 LEDs to produce various observation modes; its amber LED enables the visualization capabilities of RDI technology. LEDs have a longer life span than a xenon lamp and consume less energy.14
BAI-MAC™ Technology
Brightness Adjustment Imaging with Maintenance of Contrast (BAI-MAC) technology is an image processing function to correct the brightness of dark portions of the image while maintaining the brightness of the brighter portions of the image in order to increase visibility of distant areas. BAI-MAC technology does not accentuate halation in the image.15
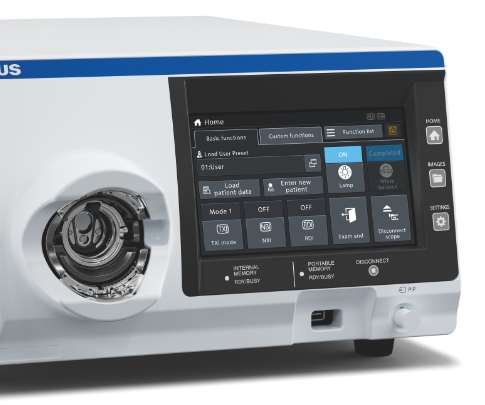
Touch Panel
The touch panel on the front of the CV-1500 video system center allows the user to initiate all procedures and settings and control image data from one device.16
Dual Focus
A two-stage optical lens technology designed to allow physicians to switch from normal to near focus mode with a single button to conduct close examination of mucosal tissue and capillary networks. When Dual Focus and NBI technology are used together, endoscopists are more likely to make high confidence predictions of diminutive polyp histology than those using standard focus colonoscopes.17
ScopeGuide™ Technology
Provides a real-time, 3D image of the position and configuration of the colonoscope during a procedure. It is designed to help physicians recognize loops as they form, potentially decreasing insertion time and lessening patient discomfort.18
Pre-Freeze Function — Updated Algorithm
Automatically buffers a continuous, rapid series of procedural images and saves the sharpest image in the desired view. This saves time and may lessen a physician’s frustration when capturing still images.15
Integrated Water Jet
Improves the accuracy of observations and efficiency of treatment by easily removing mucus and other residues in the investigated intestinal areas.19
Waterproof One-Touch Connector
Allows one-step connection to the video system center to minimize the effort required for setup prior to and in-between cases. The connector is fully submersible, eliminating the need for a water-resistant cap during reprocessing. It also may minimize the repair costs to the connector.20

EVIS X1 Endoscopy System Atlas
Explore real-life cases using EVIS X1 technologies in the EVIS X1 Endoscopy System Atlas on the Olympus Continuum™ training platform.



TXI™ Technology is 510(k) cleared in the United States. This study is being furnished to provide data results from this study that are related to the TXI Technology. Products used in this study are not available in all countries. There is no time period established as to when or if these products will be available in these markets, including the United States. The safety and effectiveness for these products and/or the use of some of these products has not yet been established in the United States market.


Gastroenterologist Dr. Gareth Corbett, MD, from Cambridge, England, shares his experience with the EVIS X1 endoscopy system and discusses cases where he used RDI technology to help find and stop active bleeding.
Complete this form to get the latest information about the EVIS X1 endoscopy system.
The EVIS X1 endoscopy system is not designed for cardiac applications. Other combinations of equipment may cause ventricular fibrillation or seriously affect the cardiac function of the patient. Improper use of endoscopes may result in patient injury, infection, bleeding, and/or perforation. Complete indications, contraindications, warnings, and cautions are available in the Instructions for Use (IFU).
This site is published by Olympus America Inc., which is solely responsible for its contents and is intended for U.S. audiences only. Not all products are available for sale in all markets.
This site is intended for Healthcare Professionals. If you are a patient, it is important that you discuss information about the benefits and risks of products with your doctor.
EDOF, TXI, RDI, NBI and BAI-MAC are trademarks of Olympus Corporation, Olympus America, Inc., and/or their affiliates.
1. Data on file with Olympus (DC00303282).
2. Data on file with Olympus (DC00493386, DC00433276, DC00510434 and DC00567392).
3. Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M, et al. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 2017;66(4):683-691.
4. Corley DA, Jensen CD, Marks AR, et al. Adenoma detection rate and risk of colorectal cancer and death. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(14):1298-1306.
5. Data on file with Olympus (DC00489968).
6. Young E, Rajagopalan A, Tee D, et al. Texture and color enhancement imaging improves colonic adenoma detection: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2024;166(2):338-340.e3.
7. Data on file with Olympus (DC00785702).
8. Parker, D. R., Luo, X., Jalbert, J. J., Assaf, A. R. (2011). “Impact of upper and lower gastrointestinal blood loss on healthcare utilization and costs: a systematic review.” Journal of Medical Economics, 14(3), 279-287. doi: 10.3111/13696998.2011.571328.
9. Data on file with Olympus as of 07/02/2010.
10. Atkinson NSS, Ket S, Bassett P, et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:462–71.
11. Aziz M, Fatima R, Lee-Smith W, Khuder S, Nawras A. “Comparing endoscopic interventions to improve serrated adenoma detection rates during colonoscopy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.” Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;32(10):1284-1292. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001844.
12. Data on file with Olympus as of 07/17/2020.
13. Data on file with Olympus (DC00482729, DC00600786, DC00031984, DC00482747, DC00482867, DC00600794, DC00481878, DC00031984 and DC00841888).
14. Data on file with Olympus (DC00412083 and DC00623365).
15. Data on file with Olympus (DC00436067).
16. Data on file with Olympus (DC00460933).
17. Kaltenbach, T. et al. “Real-time optical diagnosis for diminutive colorectal polyps using narrow-band imaging: The VALID randomized clinical trial.” Gut. 2015. 64: 1569:1577.
18. Data on file with Olympus as of 07/Mar/2014.
19. Data on file with Olympus (DC00485027 and DC00482967).
20. Data on file with Olympus (DC00485420, DC0047916 and DC00474352).


























-Technology.png)





