Olympus announces acquisition of Arc Medical Design Limited from Norgine B.V.
TOKYO, (August 7, 2020) – Olympus Corporation today announced it has signed a definitive agreement to acquire Arc Medical Design Limited (Arc Medical Design), a subsidiary of Norgine B.V. The acquisition underscores Olympus' commitment to expanding its offering in gastrointestinal therapeutic devices and the development of advanced colonoscopy tools through M&A (mergers and acquisitions) opportunities as well as through R&D (research and development) with the overarching goal of improving early detection and treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC).
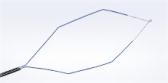
Under the agreement Olympus will acquire Arc Medical Design and obtain full rights to its suite of innovative medical products. Olympus will convert its current exclusive distribution rights of ENDOCUFF VISION™ to a full acquisition of the ENDOCUFF family of products, which also includes ENDOCUFF™, ENDOCUFF GLIDE™ and ENTEROCUFF™, as well as WIDE-EYE™ POLYTRAP and several products currently in development.
By acquiring Arc Medical Design, Olympus is assuming worldwide responsibility for design, manufacturing, distribution and business strategy for the product portfolio with an immediate effect. It will further enable the company to improve clinical outcomes, reduce overall costs and enhance quality of life for patients.
"It is a great pleasure to announce our acquisition of Arc Medical Design", said Mike Callaghan, Vice President/General Manager of Global GI EndoTherapy Business Unit at Olympus. "ENDOCUFF VISION has been a pivotal tool in our EndoTherapy portfolio, and we are delighted to expand our product portfolio to include the entire ENDOCUFF family."
The flagship product ENDOCUFF VISION is a device attached to the distal end of a colonoscope, designed to maintain and maximize visibility during colonoscopy. Through its unique design, ENDOCUFF VISION can manipulate large folds, anchor the scope tip during loop reduction and stabilize during complex procedures, such as a polypectomy.
Data has shown a colonoscopy with ENDOCUFF technology can increase the adenoma detection rate (ADR) by up to 11% compared to a standard colonoscopy1. Research shows that, for every 1% increase in ADR, there is a 3% decrease in CRC risk2. Higher detection rates and more accurate diagnosis could, therefore, help reduce the number of deaths from preventable digestive cancers, such as CRC. CRC is a leading cause of cancer death for both men and women and screening is one of the powerful weapons against the disease. Colonoscopy is considered the beneficial method for detection and removal of hard-to-find adenomatous polyps.
Callaghan sums up: "We are excited about the acquisition of Arc Medical Design as it expands our expertise in innovative medical technology, strengthens our global leadership in endoscopy and reinforces the commitment to our purpose of making people's lives healthier, safer and more fulfilling."
# # #
About Olympus' Therapeutic Solutions business
In its Therapeutic Solutions business, Olympus uses innovative capabilities in medical technology, therapeutic intervention, and precision manufacturing to help healthcare professionals deliver diagnostic, therapeutic, and minimally invasive procedures to improve clinical outcomes, reduce overall costs, and enhance the quality of life for patients. Starting with its early contributions to the development of the polypectomy snare, Olympus' Therapeutic Solutions portfolio has grown to include an array of surgical energy devices and a wide range of instruments to help prevent, detect, and treat disease. For more information, visit www.olympus-global.com.
1 Williet, N., Tournier, Q., et al. Effect of Endocuff-assisted colonoscopy on adenoma detection rate: meat-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Endoscopy, 50(9), 846-860. Doi: 10.1055/a-0577-3500. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29698990
2 Corley DA, Jensen CD, Marks AR, et al. Adenoma Detection Rate and Risk of Colorectal Cancer and Death. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370:1298–1306. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4036494/