CMS Publishes Final Category I CPT Codes and Reimbursement Rates for the iTind™ Procedure
CENTER VALLEY, Pa., (November 7, 2024) – Olympus Corporation, a global medical technology company committed to making people's lives healthier, safer, and more fulfilling, is pleased to announce today that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have published the final Category I Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) codes and code descriptions and CY2025 Medicare reimbursement rates for the iTind™ urological procedure as part of the CMS CY2025 fee schedules. The new codes and rates go into effect January 1, 2025.
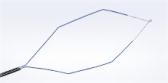
The iTind procedure is a minimally invasive treatment for men with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Two new codes, one for insertion (53865)1 and one for removal (53866)2 of the iTind device, have been established and will apply to all sites of service.
“This reimbursement milestone is important for men suffering the symptoms of BPH who meet the treatment criteria for the iTind procedure,” said Matt Moore, Vice President of Health Economics and Market Access for Olympus Corporation. “The new CPT codes support greater access to a proven minimally invasive treatment option for enlarged prostate that relieves urinary symptoms3,4,5 and helps men regain their quality of life. Additionally, the new codes may help streamline the billing process and potentially reduce administrative burden for health care providers.”
About the iTind procedure
The iTind procedure involves the placement of a temporarily implanted nitinol device that reshapes the prostatic urethra without burning or cutting out the prostate. The device can be placed in an outpatient setting or physician office. It remains in place for five to seven days while the patient is at home. Upon removal, the iTind procedure provides rapid and effective relief of LUTS symptoms6,7,8 with long-term durable results.9 In studies, treatment with the iTind procedure did not affect sexual and ejaculatory function1,2,3 or urinary continence.3
As with any medical procedure, there are potential risks. Implantation of the iTind™ device may cause pelvic discomfort, blood in urine, painful or urgent urination. In rare cases, the iTind device may cause urinary tract infection or a sudden difficulty to urinate. The iTind procedure is indicated for men aged 50 and above.
“Our clinical research continues to show benefits of the iTind procedure, and our healthcare providers are very enthusiastic about the procedure as well,” said Glen Branconier, Global Vice President, Therapeutic Solutions Division, Urology Business Unit Lead for Olympus Corporation. “With the added establishment of CPT codes, we believe we will see more patients getting the relief they need and the quality of life they deserve.”
Patients who are candidates for the iTind procedure may be assisted in navigating medical insurance systems through the Olympus UNITE program. Olympus UNITE includes services such as pre-authorization, patient appeals services, and a reimbursement support helpline to support coverage, coding, and payment concerns. Healthcare providers and patients with questions about the program should email olympusunite@priahealthcare.com.
For healthcare providers, further reimbursement support may be provided by Olympus Field Reimbursement Managers who can provide additional reimbursement insight and guidance, as well as resources specific to the overall reimbursement process for the iTind procedure. An Olympus Field Reimbursement Manager can be reached via email at iTindFRM@olympus.com.
More information about the iTind procedure can be found here: BPHtherapy.com/iTind
# # #
About Olympus
At Olympus, we are committed to Our Purpose of making people’s lives healthier, safer and more fulfilling. As a global medical technology company, we partner with healthcare professionals to provide solutions and services for early detection, diagnosis and minimally invasive treatment, aiming to improve patient outcomes by elevating the standard of care in targeted disease states.
For more than 100 years, Olympus has pursued a goal of contributing to society by producing products designed with the purpose of delivering optimal outcomes for its customers around the world. For more information, visit medical.olympusamerica.com.
Olympus Corporation of the Americas, a wholly owned subsidiary of Olympus Corporation, is headquartered in Center Valley, Pennsylvania, USA, and employs more than 4,500 employees throughout locations in North and South America. For more information, visit olympusamerica.com.
CPT disclaimer: The American Medical Association (AMA) is responsible for development and maintenance of Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) codes. Providers should check the complete AMA CPT code book for a complete listing of all CPT codes and their descriptors. It is the provider’s responsibility to report the code(s) that accurately describes the procedure(s) furnished and the patient’s diagnosis. Please note that the presence of a code, or billing a particular code, is not a guarantee of payment. Reimbursement will vary for each provider based on a number of factors, including the payer, site of service, geographic location and contractual terms.
CPT codes, descriptions, and other data only are copyright (2023) American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. Applicable FARS/HHSARS apply. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the AMA, are not part of CPT, and the AMA is not recommending their use. The AMA does not directly or indirectly practice medicine or dispense medical services. The AMA assumes no liability for data contained or not contained herein.
1. Category I CPT Code 53865 Description: Cystourethroscopy with insertion of temporary device for ischemic remodeling (i.e., pressure necrosis) of bladder neck and prostate
2. Category I CPT Code 53866 Description: Catheterization with removal of temporary device for ischemic remodeling (i.e., pressure necrosis) of bladder neck and prostate
3. Chughtai, B; Elterman, D; Shore, N; et al. “The iTind Temporarily Implanted Nitinol Device for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial.” Journal of Urology, pub. July 2021
4. Elterman, D; Alshak, M; Martinez Diaz, S; et al. “An Evaluation of Sexual Function in the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Men Treated with the Temporarily Implanted Nitinol Device.” Journal of Endourology, pub. December 2022
5. De Nunzio C, Cantiello F, Fiori C, et al. Urinary and sexual function after treatment with temporary implantable nitinol device (iTind) in men with LUTS: 6-month interim results of the MT-06-study. World J Urol. 2021
6. Chughtai, B; Elterman, D; Shore, N; et al. “The iTind Temporarily Implanted Nitinol Device for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial.” Journal of Urology, pub. July 2021
7. Elterman, D; Alshak, M; Martinez Diaz, S; et al. “An Evaluation of Sexual Function in the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Men Treated with the Temporarily Implanted Nitinol Device.” Journal of Endourology, pub. December 2022
8. De Nunzio C, Cantiello F, Fiori C, et al. Urinary and sexual function after treatment with temporary implantable nitinol device (iTind) in men with LUTS: 6-month interim results of the MT-06-study. World J Urol. 2021
9. Amparore, D; De Cillis, S; Schulman, C; Kadner, G; Fiori, C; Porpiglia, F. “Temporary implantable nitinol device for benign prostatic hyperplasia-related lower urinary tract symptoms: over 48-month results.” [published online ahead of print, 2023 Jun 23]